variable head permeability test for soil|coefficient of permeability chart : online sales Understanding the Variable Head Permeability Test of Soil. Permeability, or the ability of soil to let water flow through its pores, is a crucial property for geotechnical engineers. This test helps . web31 de dez. de 2022 · Welcome Offer for new Borgata Online Casino accounts; includes $20 Bonus Dollars and a 100% deposit match, up to $1,000. Promotion Period: The offer is valid through December 31, 2022. Eligibility: New Borgata Online Casino accounts only (no prior accounts, wagering or deposits).
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB3 de out. de 2019 · Fernandinho - As 30 Melhores01 - 00:00:00 - Alvo Mais Que a Neve02 - 00:04:44 - Jesus, Filho de Deus03 - 00:09:55 - Pai de Multidões04 - 00:14:30 - Sou Feliz.
falling head vs constant permeability
Variable head permeability test is one of several techniques by which the permeability of soil is determined. It is used to evaluate the permeability of fairly less previous soil. Permeability is the measure of the ability of soil to allow .For the relatively permeable soils and rocks of interest in groundwater lowering problems, variable head tests can be analysed using the work of Flvorslev (1951), which is one of the methods included in the British Standards on .Understanding the Variable Head Permeability Test of Soil. Permeability, or the ability of soil to let water flow through its pores, is a crucial property for geotechnical engineers. This test helps .Constant Head Permeameters measure the coefficient of permeability of non-plastic soils with no more than 10% of particles passing a 75µm (No. 200) test sieve. The procedure described in AASHTO T 215 is also a withdrawn .
Soil permeability testing. This technique reveals the hidden features of soil, offering special soil testing information about water flow and retention which are important for effective soil management. TL;DR. We aim . Soil permeability tests fall into two main categories: laboratory and field tests. Laboratory tests, such as the constant head and variable head permeameter tests, are controlled and precise. They’re ideal for granular soils .
Indian Mahogany moisture meter
Chapter 48 - Falling head - Variable Head Permeability MethodThe property of the soil which permits the water or any liquid to flow through it through its vo. Variable-head permeability tests are often conducted in the field to determine local hydraulic conductivity values for soils. Many methods were developed over the years to interpret such tests. For determination of the permeability of a soil specimen by the variable head permeameter. Theory. The variable head permeameter is utilized to compute the permeability of comparatively less porous soils. The coefficient of permeability is expressed by: Where, = initial head, = final head, t= time interval, a= cross-sectional area of the liquid .It is good to have an idea about the order of magnitude for the permeability of a specific soil type. 7.5 LABORATORY DETERMINATION OF PERMEABILITY Permeability of a coarse grained soil can be determined by a constant head permeability test (AS1289.6.7.1-2001; ASTM D2434), and in a fine grained soil, falling head permeability test
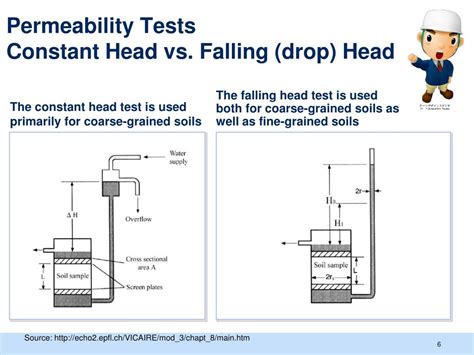
any testing is performed. PART I. CONSTANT-HEAD PERMEABILITY TEST METHOD A. SCOPE. The permeability test is a measure of the rate of the flow of water through soil. In this test, water is forced by a known constant pressure through a soil specimen of known dimensions and the rate of flow is determined. This test is used primarily toConstant/Falling Head Permeability Test Sets test granular soil samples using either constant-head or falling-head methods. The Permeameters are available in a range of specimen sizes. Shelby Tube Permeameter enables permeability testing directly on undisturbed soil samples remaining in cut-to-length sections of 3in (76mm) diameter Shelby Tubes.
Question: 3. For a variable head permeability test shown, the following are given: 200 mm. Length of soil specimen L: X-sectional area A of soil specimen: 1000 mm2 X-sectional area a of standpipe: Head difference ho at time t O: Head difference h, at time t 180 sec: 300 mm. 40 mm2 500 mm. Determine the coefficient of permeability k on the soil in (cm/sec)permeability of soil governs the type of soil to be used. 0.4 This Standard ( Part 17) covers both constant head and falling head tests as used for most of the soil. . Glass stand pipes for falling head (variable head ) test arrangement, varying in diameter from 5 to 20 mm, suitably mounted on stand or otherwise fixed on wall. . Field testing equipment for soil permeability includes constant/falling head test sets, shelly tube parameters, and flexible wall permeability test equipment. Additionally, compaction parameters, tamper, balance , scoop, graduated cylinders, .Permeability of soil can be found either in a lab or in field conditions. Important methods of permeability testing, used in both lab and field approaches are discussed further. . Falling or Variable Head Permeability Test . In this method, the water level in the stand-pipe falls continuously as water flows through the specimen. Measurement .
Laboratory test measures the coarse grained soil media and fine grained soil media that is depend upon the soil texture, types of soil , permeable ability of soil such as gravel and sand is highly permeable and it’s interconnected void space is more which is determined by constant head permeability test otherside fine grained soil such as .
Answer to 171 Problem: For a variable head permeability test, Skip to main content. Books. Rent/Buy; Read; Return; Sell; Study. Tasks. Homework help; Understand a topic; Writing & citations; Tools. Expert Q&A; . Compute the interstitial velocity under the test condition if the soil specimen has a void ratio of 0.50 in cm/sec. 3. Compute the .
Problem (2) The following data are for a variable head permeability test: Area of soil specimen=1200mm? Length of the soil specimen = 150mm Area of the standpipe = 1.3cm² At time t=0, head difference = 750mm At time t=2min, head difference = 500mm 2 %3D a) Find the hydraulic conductivity of the soil in cm/min. Falling Head Permeability Test. This is also known as the Variable head permeability test. The head-causing flow in this method is not as constant as in the previous method. The falling head permeability test is .Understanding the Variable Head Permeability Test of Soil. Permeability, or the ability of soil to let water flow through its pores, is a crucial property for geotechnical engineers. This test helps measure the permeability of soil, especially for less compacted types. The permeability impacts various aspects, such as settlement rates under .
falling head tests in borehole
Discover the process of conducting a falling head permeability test for soil mechanics on YouTube. There are several laboratories and in situ tests that can be done to estimate the permeability of the soil and every test has its own advantages and disadvantages. The two most common are “the constant head permeability method” and “the falling head permeability method”. . This method, also called the Variable Head Permeability test .
The falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, whereas the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable discharge in a given time. For very fine-grained soil, capillarity permeability test is recommended. Usually, permeability of soils is determined by two methods: 1.The test method involves variable head (rising or falling) or constant head procedures and requires knowledge of the groundwater level. The type of test undertaken depends on the soil type. . The test measures the permeability (k) of the soil and because it is carried out in-situ provides a more reliable result than can be determined in the .IIT Gandhinagar, Soil Mechanics Lab Page 1 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY GANDHINAGAR Department of Civil Engineering Soil Mechanics Laboratory Soil Lab Boss Dave Anderson demonstrates how a falling head permeability test is performed using a triaxial shear testing apparatus.
This video explains the procedure of constant head test to determine the soil permeability. This test is performed on coarse-grained soil with a high coeffic.There are two general types of permeability test methods that are routinely performed in the laboratory: (1) the constant head test method, and (2) the falling head test method. The constant head test method is used for permeable soils (k>10-4 cm/s) and the falling head test is mainly used for less permeable soils (k<10-4 cm/s).
representative sample of the complete soil prior to the perme-ability test. Any particles larger than 19 mm (3⁄4 in.) shall be separated out by sieving (Method D 422). This oversize mate-rial shall not be used for the permeability test, but the percentage of .
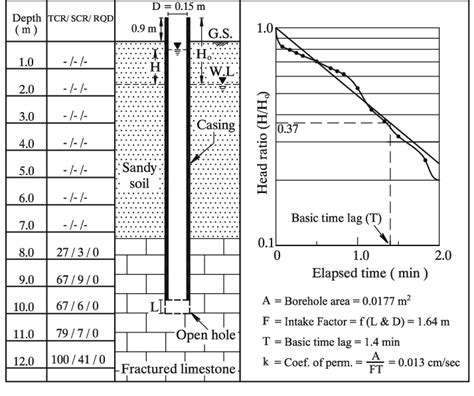
Where, K27 = Permeability at 27°C KT = Permeability at T°C μ27 = Coefficient of Viscosity at 27°C μT = Coefficient of Viscosity at T°C. 5.5 Presentation of Results: The values of permeability at T 0 C and 27 0 C are reported. Also reported are corresponding void ration, degree of saturation and water content. 6. Falling Head Test Fig. 6 shows the variation of the coefficient of permeability with depth estimated from the CPT soundings compared to the falling head test results. The values of the coefficient of permeability measured from the falling head permeability test varied between 4.21 × 10 −5 m/s and 4.11 × 10 −4 m/s, with an average value of 2.43 × 10 −4 m/s
falling head soil permeability apparatus
falling head permeability test astm
Scan this QR code to download the app now. Or check it out in the app stores
variable head permeability test for soil|coefficient of permeability chart